Welding, with its ability to join metal components with high precision and strength, plays a crucial role in modern industrial manufacturing. For decades, traditional welding methods such as MIG, TIG, and arc welding have dominated the field. However, with the growing demand for high precision, efficiency, and aesthetically pleasing weld seams, more and more manufacturers are turning to fiber laser welding machines. So, what are the key differences between these two welding methods, and how should manufacturers choose? ZS Laser shares some of our insights.
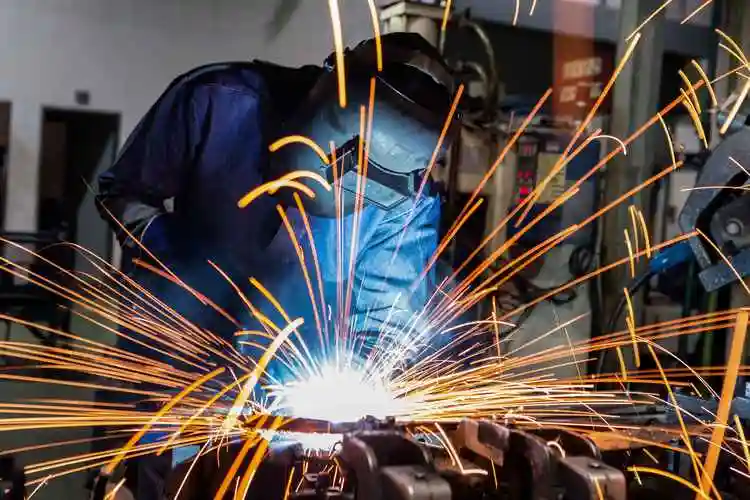

Traditional Welding Method
What is Traditional Welding?
Traditional welding covers a variety of well-established processes for joining metal parts, including TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), MIG (Metal Inert Gas), arc welding, and spot welding. For decades, these methods have been the backbone of manufacturing, widely used in industries such as automotive, construction, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery.
Advantages of Traditional Welding
Mature technology: With decades of application, traditional welding has accumulated rich practical experience. There is also a large pool of skilled operators available in the market, making the technology highly mature.
Affordable equipment: Compared with laser welding systems, traditional welding involves lower initial investment and maintenance costs.
Easy maintenance: Parts replacement and repair are simple, and there are many service providers worldwide.
Limitations of Traditional Welding
Large heat-affected zone (HAZ): Excessive heat can cause deformation of thin or delicate materials.
Warping risk: Stress from welding may lead to distortion, requiring additional post-weld treatment.
Lower welding precision: Achieving fine and uniform welds is difficult, especially with small or complex parts. The results rely heavily on operator skill, leading to inconsistent quality control.
While traditional welding remains a reliable and cost-effective solution, its limitations have driven many manufacturers to explore more precise and efficient alternatives, such as fiber laser welding.
What is Fiber Laser Welding?
Fiber laser welding is an advanced joining technology that uses a highly focused fiber laser beam to melt and fuse metals with extreme precision. Unlike traditional welding, it relies on a concentrated light source rather than an electric arc, enabling faster, cleaner, and more controllable welding.
Core Components
Fiber laser source: Provides a stable, high-power laser beam. ZS Laser typically uses sources from top manufacturers such as MAX Photonics.
Fiber delivery system: Guides the laser from the source to the welding head with minimal energy loss and high flexibility.
Welding head: Delivers the laser beam precisely onto the workpiece, often integrated with vision systems or CNC motion platforms for accurate positioning.
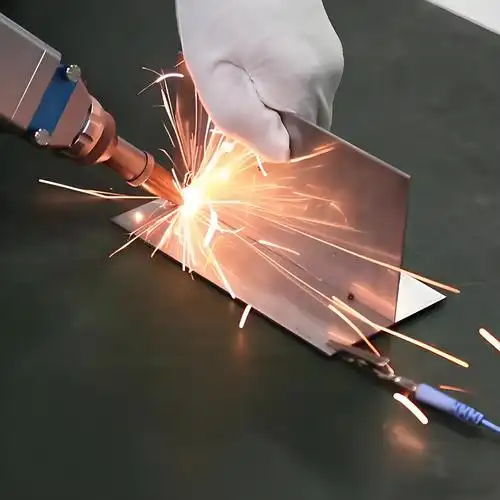

Fiber Laser Welding
Key Advantages
High precision: Capable of welding thin or complex parts with micron-level accuracy.
Minimal heat-affected zone (HAZ): Reduces deformation and preserves surrounding material integrity.
Automation-friendly: Easily integrated into robotic or automated production lines for consistent and repeatable results.
Clean and aesthetic weld seams: Smooth, fine, and visually appealing welds that reduce the need for post-processing.
Typical Applications
Fiber laser welding machines are widely used in industries where precision, speed, and reliability are critical (see specific application examples via respective links):
Automotive: Battery packs, lightweight body components, exhaust systems
Energy: Components for renewable energy systems, power generation equipment, pipelines
Tool & Die Industry: Precision dies, molds, and tooling components
Jewelry: Fine metal assembly, repair, and decorative welding
Compared with traditional methods, fiber laser welding has become the preferred solution for manufacturers pursuing higher quality, efficiency, and repeatability.
Fiber Laser Welding vs Traditional Welding
| Comparison Aspect | Fiber Laser Welding | Traditional Welding |
| Welding Quality | Smooth, precise welds; minimal spatter; usually no secondary grinding; ideal for high-end products | Rough weld seams; often require grinding or polishing |
| Efficiency&Productivity | High speed; suitable for mass production and automation | Manual-intensive; slower; lower productivity |
| Materials & Thickness | Excellent for thin metals and precise components; can weld stainless steel, aluminum, copper, etc. | Better for thick plates and large structural components |
| HeatInput&Deformation | Minimal heat-affected zone; almost no deformation | High heat input; workpieces prone to warping and distortion |
| Cost Considerations | Higher initial investment; lower long-term cost due to less labor, consumables, and post-processing | Lower upfront cost; higher ongoing costs for labor, filler materials, and finishing |
| Skill Requirements | Easy to operate; operators can train in a few days | Requires highly skilled welders with significant experience |
Which Should You Choose?
Choosing the right welding technology depends on your specific production requirements, materials, and quality expectations. There is no absolute “best” method—only the one most suitable for your application.
Fiber Laser Welding Machines: The ideal choice for high-precision, large-scale production
If your production involves mass manufacturing, precision components, or high-end products, a fiber laser welding machine is the best option. Its benefits—such as fast processing speeds, minimal heat distortion, precise and aesthetic welds, and compatibility with automation—make it ideal for industries like electronics, automotive, medical devices, and jewelry. It ensures consistent, high-quality welds, meeting strict quality standards while boosting efficiency and reducing reliance on manual labor.
Traditional Welding: Suitable for cost-sensitive and heavy-duty applications
On the other hand, if your priorities are low initial cost, thicker metals, or structural components, traditional methods (TIG, MIG, or arc welding) are more appropriate. These techniques are widely applied in construction, heavy machinery, and general manufacturing. While welds may require post-processing and lack the precision of laser welding, traditional welding remains reliable, economical, and effective for thicker and larger structures.
Choose the technology that matches your application
The key is to evaluate your production volume, material type, required precision, and budget. For some businesses, a hybrid approach may even be ideal—using traditional welding for structural parts and fiber laser welding for precision or aesthetic components. By choosing the right method for each application, you can maximize efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution. Whether you choose a fiber laser welding machine or stick with traditional welding, the best choice is the one that aligns with your production needs, product quality requirements, and overall business goals.
Looking to upgrade your welding process? Contact ZS Laser today for a free consultation and customized fiber laser welding solution.
 ZS Laser Equipment
ZS Laser Equipment

WhatsApp
Scan the QR Code to start a WhatsApp chat with us.