1. Industry Background and Processing Requirements
The Energy & Utilities sector forms the backbone of modern industry and urban operation. It includes key fields such as oil & gas, water utilities, power generation, and energy infrastructure, all of which rely heavily on large-scale piping systems and complex installations.
Across these industries, pipe processing is not only a manufacturing task but a critical factor affecting safety, system reliability, and long-term operational performance. As projects become larger and more complex, the requirements for pipe cutting accuracy, consistency, and stability continue to increase.This has led to the increasingly widespread application of laser pipe cutting machines in Energy and Utilities.

Photovoltaic power industry
1.1 Key Characteristics of the Energy & Utilities Industry
High safety standards
Oil, gas, and power systems often operate under high pressure, high temperature, or flammable conditions. Any defect at pipe joints or connections can pose serious safety risks. As a result, strict technical standards are applied to cutting accuracy, joint consistency, and structural integrity.
Long service life and high reliability requirements
Energy and utility facilities are designed for continuous operation over decades. Once pipelines are installed, maintenance and replacement costs are extremely high. This makes manufacturing quality at the early stage crucial to long-term system reliability.
Complex piping systems with diverse specifications
Real-world projects involve pipes with different diameters, wall thicknesses, and materials, as well as branch connections, holes, bevels, and multi-angle interfaces. This diversity places high demands on processing flexibility and repeatability.
1.2 The Critical Role of Pipes in Energy Applications
Oil & Gas: Pipelines are responsible for transportation, distribution, and process connections. Cutting quality directly affects sealing performance and operational safety.
Water utilities and municipal engineering: Pipes form the core of supply, drainage, and pumping systems, where durability and long-term stability are essential.
Power generation: Pipes are widely used in cooling systems, steam lines, and auxiliary equipment. Processing precision directly influences system efficiency and reliability.
These factors explain why the Energy & Utilities industry places greater emphasis not only on efficiency, but also on precision, consistency, and long-term performance in pipe processing.
2. Common Pipe Types in Energy & Utilities
2.1 Pipe Shapes
Round pipes (dominant type)
Round pipes are the most widely used in energy and utility systems due to their uniform stress distribution and suitability for high-pressure and long-distance transportation. They often require multi-angle cutting, hole processing, and branch connections with high accuracy.
Square and rectangular tubes
These are mainly used for support structures, pipe racks, platforms, and equipment frames. Structural strength and dimensional consistency are the primary concerns.
2.2 Materials
Carbon steel: The most commonly used material, offering good strength, machinability, and cost efficiency.
Stainless steel: Preferred in corrosive environments or systems with higher cleanliness requirements.
Alloy steel: Used in high-temperature or high-pressure applications, especially in refineries, chemical plants, and power systems.
2.3 Diameter and Wall Thickness Range
Energy projects involve everything from small and medium pipes to large-diameter, thick-wall pipes. This wide range requires cutting equipment that delivers both sufficient power and consistent precision across different specifications.
3. Limitations of Traditional Pipe Processing Methods
Traditional pipe processing in the energy sector typically relies on saw cutting, drilling, and manual grinding, which presents several limitations.
Multiple processes and low efficiency
Separate operations increase production time and cumulative errors.
Unstable accuracy and poor joint matching
Manual operations often result in variations in hole position, angle accuracy, and cut perpendicularity, leading to poor fit-up during assembly.
High labor dependency
Complex cuts require experienced operators, making quality difficult to standardize and scale.
Inconsistent welding quality
Irregular cut edges and gaps increase welding difficulty and affect long-term joint reliability.
High rework and risk costs
In high-standard industries such as oil, gas, and power, rework leads to higher costs, delays, and increased safety risks.
4. Core Advantages of Laser Pipe Cutting in Energy & Utilities
4.1 High Precision for Superior Joint Quality
Laser pipe cutting is a non-contact process with a small heat-affected zone and stable cut quality. The result is smooth edges, precise geometry, and excellent repeatability, providing an ideal foundation for high-quality welding.
4.2 Flexible Processing of Complex Pipe Structures
With CNC control and multi-axis motion, laser pipe cutting machines can complete branch holes, angled cuts, and complex profiles in a single setup, reducing repositioning errors and manual adjustments.
4.3 Improved Productivity and Consistency
By integrating cutting, hole-making, and beveling into one system, laser pipe cutting significantly improves efficiency while ensuring consistent results—especially suitable for project-based and small-to-medium batch production.
4.4 Reduced Secondary Processing and On-site Installation Work
High cut quality minimizes grinding and rework before welding and installation, shortening construction cycles and lowering overall project costs.
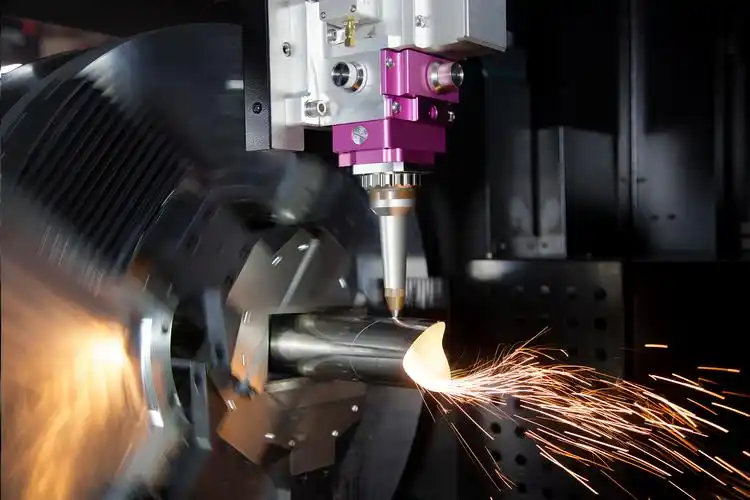

Laser Pipe Cutting Process
5. Typical Application Scenarios
Oil & Gas Pipelines
Transport pipeline connections
Prefabricated branch joints
Pipe support structures
Water Utilities and Municipal Engineering
Water supply and drainage pipelines
Pump station piping systems
Pipe racks and support frames
Refineries and Chemical Plants
Process pipelines
High-temperature and high-pressure pipe components
Equipment connection pipes
Power Plants and Energy Infrastructure
Cooling and steam systems
Boiler and auxiliary equipment piping
Platforms and structural supports
6. Recommended Laser Pipe Cutting Configurations for Energy Applications
6.1 Laser Source Type
Fiber lasers are the preferred choice due to stable beam quality, high energy efficiency, and low maintenance—ideal for carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel pipes in continuous industrial operation.
6.2 Power Range by Application Level
2–3 kW: General pipelines, municipal projects, and structural tubes
3–6 kW: Thick-wall pipes, high-strength materials, oil & gas, power and chemical applications
6.3 Clamping and Rotation System
High-precision clamping and stable rotation are essential to ensure accurate hole cutting, beveling, and multi-angle processing.
6.4 Structural Design for Heavy Pipes
Processing large-diameter and thick-wall pipes requires a rigid machine structure, reinforced bed, and stable motion system to maintain accuracy under heavy loads.
6.5 Long-term Stability and Reliability
Energy projects demand equipment that performs consistently over long operating cycles. Stability directly affects quality control, maintenance cost, and project schedules.
7. Why Laser Pipe Cutting Is Being Increasingly Adopted in the Energy Industry
Shift toward standardization and prefabrication
Higher requirements for construction efficiency and safety
Continuous improvement in laser system stability and cost-effectiveness
Proven global adoption of laser processing in large infrastructure projects
Laser pipe cutting is no longer a niche technology—it is becoming a mainstream manufacturing solution for modern energy infrastructure.
8.Choosing the Right Laser Pipe Cutting Solution for Energy & Utilities
As a dedicated manufacturer and solution provider, ZS Laser focuses on delivering stable, reliable laser pipe cutting solutions tailored for complex Energy & Utilities applications. We understand the industry’s strict requirements for safety, consistency, and long-term performance, and design our machines with real engineering conditions in mind.
Whether you are involved in oil & gas pipeline fabrication, municipal water projects, or energy infrastructure manufacturing, ZS Laser can provide professional machine selection advice and customized solutions to help you improve efficiency, reduce risk, and achieve stable long-term operation.
Contact ZS Laser to explore how laser pipe cutting technology can support your Energy & Utilities projects.
We look forward to contributing to the future of high-quality energy infrastructure.
 ZS Laser Equipment
ZS Laser Equipment




WhatsApp
Scan the QR Code to start a WhatsApp chat with us.