When choosing a laser welder, many customers face a common challenge: the market offers a wide variety of machines, with complex parameters and very different appearances, making it difficult to know where to begin. Which type is truly suitable for your production needs?
At ZS Laser, we have been deeply engaged in the laser equipment field for more than ten years. We have helped many domestic and international clients find the right laser equipment for their needs. Below, I will share my understanding of laser welders to help you make the best choice in the future.
Laser welders come in many types, which can generally be classified as follows:
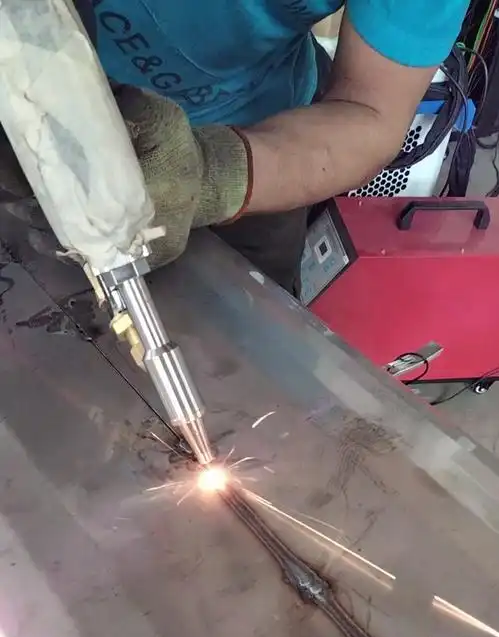

Handled Laser Welding Process
By Laser Type
Fiber Laser Welder
Fiber laser welders are currently the most widely used type. They generate high-quality beams using rare-earth-doped fiber cables.
Advantages: High energy conversion efficiency (up to 40%), low maintenance cost, long lifespan (over 100,000 hours), excellent beam quality.
Applications: Suitable for welding stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, copper, and other metals. Widely used in sheet metal processing, automotive parts, battery manufacturing, and precision instruments.
CO₂ Laser Welder
CO₂ laser welders generate infrared light at a wavelength of 10.6 μm using a carbon dioxide gas mixture. Before fiber lasers became widespread, CO₂ laser welders occupied a large market share. After fiber lasers became popular, they were rarely used for metals, but can still occasionally be applied in some non-metal fields.
Advantages: Good absorption by non-metal materials, wide working range.
Applications: Suitable for welding plastics, glass, and some thin metals. While use in metal processing has decreased, they still have applications in non-metal industries.
Solid-State Laser Welder
Solid-state laser welders (commonly Nd:YAG) use crystals or glass rods as the gain medium.
Advantages: High peak power, short pulses, suitable for spot welding and seam welding.
Applications: Widely used in electronics, medical devices, and precision mechanical parts for high-precision spot welding.
Diode Laser Welder
Diode laser welders use semiconductor laser diodes as the light source.
Advantages: Compact structure, high electrical efficiency, low cost.
Limitations: Beam quality is weaker than fiber lasers.
Applications: Suitable for micro-welding, plastic welding, biomedical components, and small consumer electronics.
UV Laser Welder
UV laser welders operate at a wavelength of 355 nm.
Advantages: Extremely small heat-affected zone, ideal for fine and sensitive materials.
Applications: Used for plastic micro-welding, precision electronics, thin films, and high-value medical devices.
By Operation Mode
At ZS Laser, laser welders are also categorized by operation mode:
Handheld Laser Welder
A handheld laser welder consists of a cabinet with wheels for mobility and a laser gun that operators hold during welding. In recent years, handheld laser welders have quickly become popular due to their flexibility and ease of use, becoming the preferred upgrade for many small factories.
Advantages: Easy to move, simple to operate, no need for highly professional welding operators—ordinary workers can be trained to use it proficiently.
Applications: Suitable for welding sheet metal, pipes, stainless steel doors and windows, hardware, and also for welding large immovable workpieces.
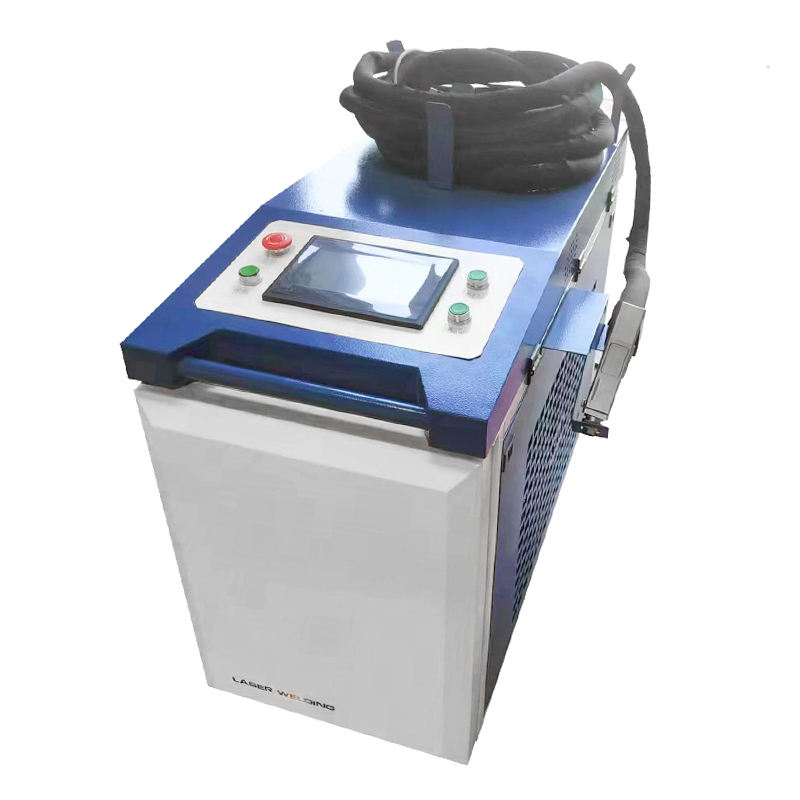

Handled Laser Welder
Desktop Laser Welder
Compared with handheld types, desktop laser welders include a welding platform, usually a workbench. They come in both manual and automatic operation modes. In manual mode, the operator places the workpiece and moves the welding module into position. In automatic mode, operators simply place the workpiece, and with one click the machine completes the welding task based on pre-programmed settings.
Advantages: Fixed workstations ensure high precision and consistency. Often equipped with microscopes or cameras to monitor weld quality in real time. Suitable for micro-welding.
Applications: Jewelry welding, mold repair, dental instruments, watch parts, small electronics, and laboratory research.
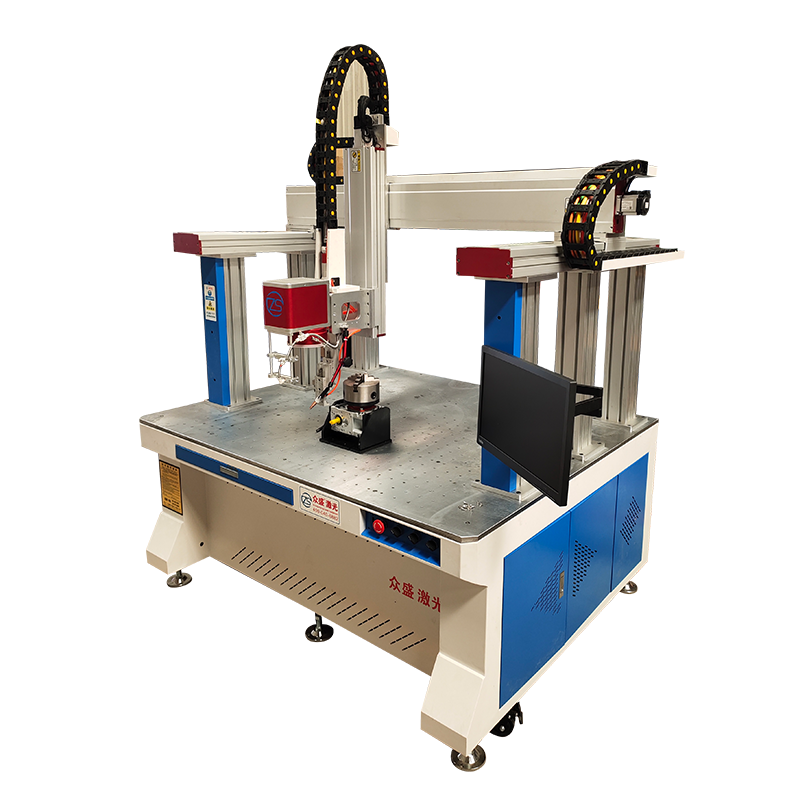

Desktop Laser Welder
Robotic Laser Welder
Modern robotic laser welders essentially combine multi-axis robotic arms with laser sources, enabling 360° all-angle welding. They can be integrated into production lines, running 24/7 without human intervention once programmed.
Advantages: Capable of 360-degree, multi-angle welding, fully automated, suitable for mass production.
Applications: Automotive bodies, aerospace components, pipelines, heavy machinery, and large-scale manufacturing.
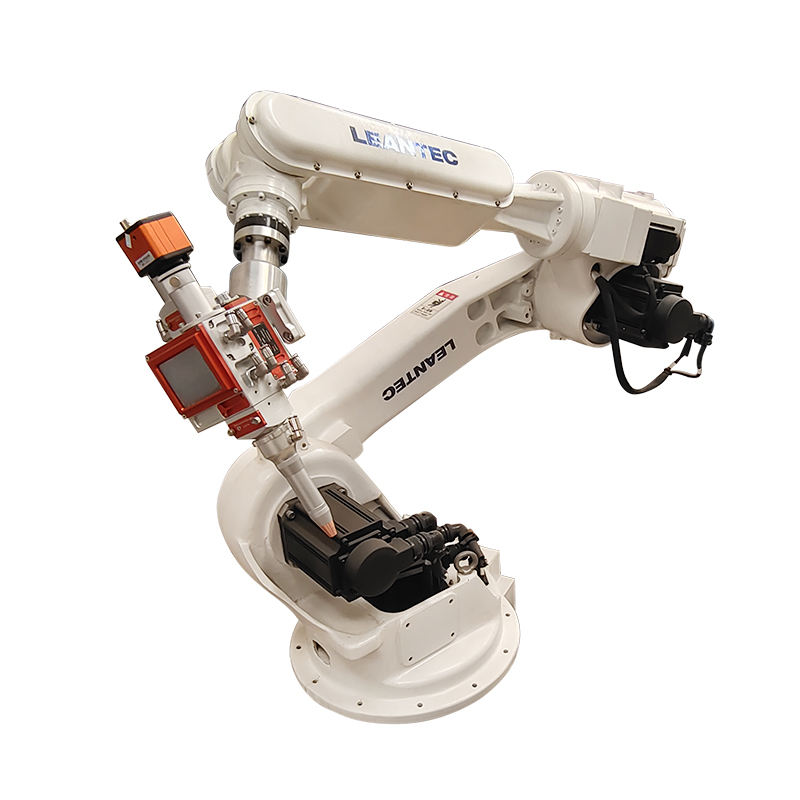

Robotic Laser Welder
By Welding Process
Laser welders can also be divided by welding process:
Spot Welding
Principle: Short-pulse lasers form precise weld spots.
Applications: Electronic components, batteries, sensors, and connectors.
Seam Welding
Principle: Continuous laser beams form long and stable weld seams.
Applications: Pipes, fuel tanks, and sealed containers.
Overlap Welding
Principle: Welding at overlapping sections of thin metal sheets.
Applications: Thin sheet processing, automotive body panels, air-conditioning pipelines.
Penetration Welding
Principle: High-power lasers completely penetrate thick materials, forming deep weld seams.
Applications: Structural steel, aerospace frames, heavy equipment.
Conduction Welding
Principle: Low-power lasers heat only the surface, without forming deep melt pools.
Applications: Workpieces with high surface-quality requirements, such as electronics and decorative items.
By Power and Application
Low-Power Laser Welders (<500W)
Applications: Precision welding of electronics, jewelry, medical devices, and miniature parts.
Features: Minimal heat effect, shallow weld depth, high precision.
Medium-Power Laser Welders (1000–2000W)
Applications: Sheet metal, hardware, furniture, and general manufacturing.
Features: Balanced penetration and efficiency, suitable for small to medium-sized factories.
High-Power Laser Welders (>2000W)
Applications: Automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, heavy machinery.
Features: Capable of welding thick plates and large structural parts, with deep penetration and high efficiency.
The above is the general classification of laser welding machines. After understanding these classifications, you can better determine your needs when purchasing products.
Are you looking for a laser welder that meets your production needs?
Contact ZS LASER today, tell us your welding requirements, and get expert advice, customized configurations, and efficient solutions.
 ZS Laser Equipment
ZS Laser Equipment

WhatsApp
Scan the QR Code to start a WhatsApp chat with us.