What is Metal Prefabrication
Metal prefabrication refers to the entire process of pre-processing metal materials before metal products enter the final assembly or construction stage. It typically includes cutting, drilling, bending, welding, marking, surface treatment, and other steps, aiming to ensure that metal components meet the design dimensions and structural requirements before assembly.
In the past, metal prefabrication largely relied on manual cutting and traditional machining, which not only had low efficiency and high errors but also wasted a large amount of material. With the development of digital manufacturing and automated equipment, modern metal prefabrication is undergoing a revolutionary change.
Among them, the introduction of laser technology has become the core driver of this transformation. Whether it is laser cutting, laser welding, or laser marking, tasks that were previously impossible with traditional methods can now be completed with higher precision, higher speed, and lower energy consumption. Laser equipment enables metal prefabrication to transition from “manual experience-based manufacturing” to “intelligent precision manufacturing.”
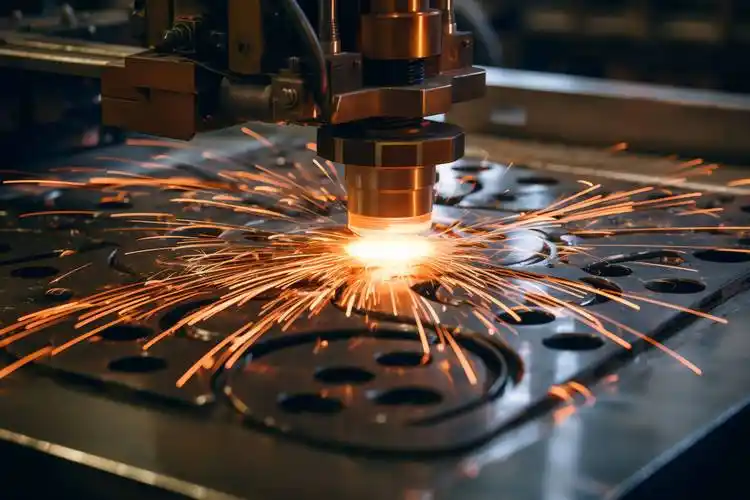

Metal board Laser Cutting
Main Process Steps in Metal Prefabrication
Metal prefabrication is not a single process, but a complete, systematic, and continuous production workflow. From raw material preparation to the final structural assembly, each step directly affects the precision, strength, and assembly efficiency of the finished product. The following are the most critical process steps in metal prefabrication and their commonly used methods:
Metal Cutting
Cutting is the starting point of metal prefabrication and one of the most fundamental and core steps in the entire workflow. It determines the dimensional accuracy and structural compatibility of subsequent assemblies. Common cutting methods include:
1.Saw Cutting: Simple equipment, suitable for thick plates and small batch production, but with rough edges and large errors.
2.Oxy-fuel Cutting: Can cut thicker carbon steel plates, but has a large heat-affected zone and obvious deformation.
3.Plasma Cutting: Fast and versatile, but slag is present at the cutting edge and requires post-processing.
4.Waterjet Cutting: Cold cutting method that avoids thermal deformation, but at higher cost.
5.Laser Cutting: Uses a high-energy-density beam for high-precision cutting, with smooth edges and minimal heat impact. The cut pieces can be directly used for subsequent assembly, making it the current mainstream high-end cutting method.
Drilling & Punching
Drilling and punching are essential steps in metal prefabrication, used to process bolt holes, sockets, ventilation holes, and installation slots. Common methods include:
1.Drilling Machines: Suitable for thicker workpieces but slow, and hole accuracy depends on manual positioning.
2.Punching Machines: Suitable for mass production, fast, but with high die cost and fixed hole shapes.
3.Laser Cutting + Drilling: Can complete cutting, drilling, chamfering, and other tasks in one operation, especially suitable for composite parts in automated production lines.
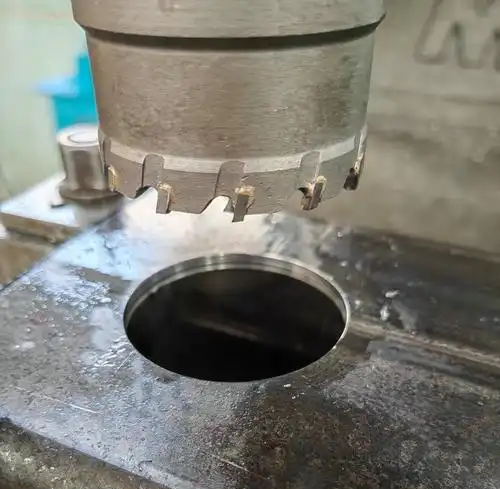

Metal punching pictures
Bending & Forming
Bending transforms flat metal sheets into three-dimensional structures. Common equipment and methods include:
1.Manual Bending Machines: Suitable for single-piece or prototype processing.
2.CNC Press Brake: Program-controlled angle and position, high precision and consistency, main equipment for modern prefabrication production.
3.Rolling & Stretch Forming: Used for large curved surfaces or tubular structures, such as tanks, frames, or protective covers.
Welding & Assembly
Welding connects various prefabricated parts into frames or complete structures, a key step from component processing to structural assembly. Common welding methods include:
1.Manual MMA Welding: Simple equipment but low efficiency, weld quality highly dependent on operator skill.
2.MIG/TIG Welding: Beautiful welds, high strength, suitable for stainless steel and aluminum alloys.
3.Resistance Welding: Commonly used for thin sheet and spot welding.
4.Laser Welding: Concentrated energy, fine welds, minimal heat-affected zone, suitable for high-precision assemblies.
Surface Finishing & Marking
Before prefabricated parts enter assembly or coating, surface treatment is usually required to improve corrosion resistance, aesthetics, and adhesion for subsequent processes. Common methods include:
1.Deburring & Polishing: Removes burrs and edges after cutting or welding, improving surface smoothness.
2.Sandblasting & Coating: For corrosion protection and surface decoration.
3.Electroplating & Anodizing: Enhances surface hardness and oxidation resistance.
4.Marking: Marking of QR codes, serial numbers, or logos on metal surfaces, enabling traceability and brand recognition.
Through the coordination of these steps, metal prefabrication achieves the complete transformation from “raw material” to “assembly-ready components.” A complete metal prefabrication system can significantly improve production efficiency and processing accuracy, while enabling flexible production and intelligent management.
Applications of Laser Equipment in Metal Prefabrication
With the development of intelligent manufacturing and precision processing, modern metal prefabrication increasingly requires “high precision, high efficiency, and high consistency.” Laser equipment can be applied across multiple key steps—cutting, welding, marking, rust removal, and positioning—covering almost the entire pre-shaping processing chain of metal components.
Laser Cutting: High-Precision Starting Point
Cutting is the first step in metal prefabrication, determining the accuracy of subsequent welding and assembly. Laser cutting machines use high-energy-density beams for non-contact cutting of metal sheets and tubes, easily handling carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloys, copper, and other materials.
Technical Advantages:
Cutting accuracy up to ±0.05mm, smooth edges, no secondary grinding required;
Minimal heat-affected zone, avoiding material deformation;
Combined with CNC systems, can automatically cut arbitrary shapes, and with automatic feeding systems, greatly reduces manual labor;
Drilling can also be performed simultaneously during cutting, avoiding secondary processing;
Ensures high precision and consistency for structural steel cutting in construction or tube hole processing in automotive chassis.
Laser Welding: Efficient Core Connection
Welding is key when prefabricated parts enter the assembly stage. Laser welding uses a focused high-energy beam for deep penetration in a small area, with high energy density, narrow welds, and minimal deformation.
Typical Advantages:
High-strength, smooth, and aesthetic welds;
Low heat input, almost no deformation, suitable for thin-walled structures;
Compatible with robotic systems for multi-axis automatic welding;
Applicable for spot, seam, and joint welding.
Laser welding is increasingly replacing traditional arc welding in automotive prefabrication, mechanical frames, and agricultural machinery piping, becoming a core technology for automated assembly lines.
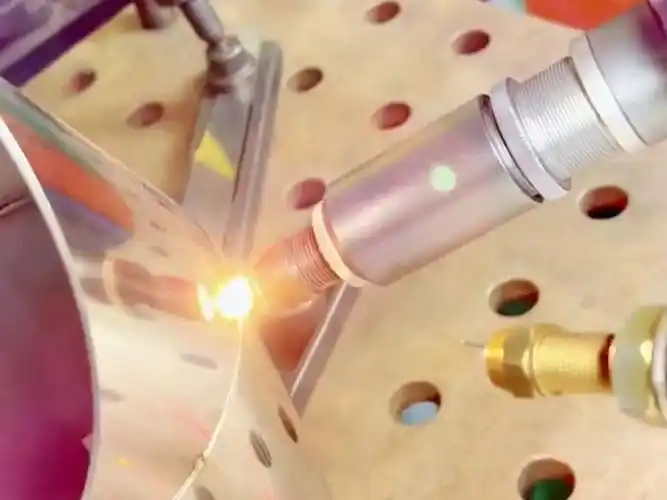

Automobile exhaust pipe laser welding
Laser Marking: Information & Quality Assurance
At the final stage of metal prefabrication, parts often require numbering, traceability, branding, or batch marking. Laser marking machines use high-energy beams to permanently engrave metal surfaces, producing precise, wear-resistant, and durable marks.
Applications:
Product traceability (serial numbers, QR codes, batch numbers);
Part identification (model, specification, installation direction);
Company logos, assembly instructions, etc.
Compared to inkjet or label marking, laser marking requires no consumables, is unaffected by paint or oxidation layers, and maintains clarity over time.
Laser Rust Removal & Surface Cleaning: Preprocessing Upgrade
Metal materials often develop rust, oil, or coating residues due to oxidation or storage. Traditional cleaning methods (sandblasting or chemical solvents) may cause dust pollution or material damage. Laser cleaning uses high-energy pulses to vaporize surface contaminants, achieving green, non-contact cleaning.
Advantages:
No chemical agents, environmentally friendly;
Does not damage the base material, uniform cleaning;
Suitable for steel, aluminum, copper, and other metals;
Can be integrated into production lines for automated cleaning and preprocessing.
This is particularly important for shipbuilding, steel structures, and automotive prefabrication corrosion treatment.
Laser Positioning & Auxiliary Marking: Assembly Precision Enhancement
In bending, assembly, or welding, part positioning directly affects weld quality and structural alignment. Laser positioning systems use red or visible light projection for fast positioning, marking, and assembly assistance.
Common Applications:
Angle positioning and marking before bending;
Part positioning guidance in welding fixtures;
Visual assistance and inspection on assembly lines.
Laser positioning greatly reduces manual measurement errors, improving production consistency and line efficiency.
ZS Laser Provides Comprehensive Laser Solutions for Metal Prefabrication
In metal prefabrication, equipment advancement directly affects production efficiency and product quality. ZS Laser, as a professional laser equipment manufacturer, is committed to providing users with high-precision, high-reliability laser processing solutions, helping enterprises achieve automation and high-quality production in a competitive manufacturing environment.
Core Equipment of ZS Laser
Laser Tube Cutting Machine:
Suitable for high-speed cutting of round, square, rectangular, and special-shaped tubes, capable of engraving, drilling, slotting, beveling, and end-face processing. Smooth edges, high precision, widely used in construction steel structures, automotive manufacturing, agricultural machinery, furniture, fitness equipment, and metal crafts.
Laser Welding Machine:
Supports deep welding, spot welding, seam welding, and joint welding, with smooth, aesthetic welds and minimal deformation. Supports handheld, platform automation, and robotic welding modes, ideal for thin-walled metal structures, tubes, brackets, and frames.
Laser Marking Machine:
Permanently marks carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloys, copper, galvanized plates, etc., capable of text, QR codes, logos, and batch numbers, widely used for part traceability, brand identification, and anti-counterfeiting.
Key Metal Prefabrication Tasks Achievable with ZS Laser Equipment
Tube cutting & forming: precise and fast cutting and hole processing of metal tubes.
Drilling & beveling: integrated hole and bevel processing during cutting, improving assembly accuracy.
Welding & joining: high-strength, low-deformation metal welding for structural assembly.
Metal marking & engraving: high-contrast, wear-resistant marking for traceability and quality control.
Surface rust removal & cleaning: laser cleaning removes oxidation, oil, and coating residues without damaging the base material.
If you are looking for a high-efficiency, high-precision metal prefabrication solution, ZS Laser equipment will help you achieve production automation and quality upgrades. Whether you need cutting, welding, marking, or rust removal, we provide complete support for your metal manufacturing.
Contact us today for free sample testing and process consultation, and discover how laser technology can optimize your production workflow.
 ZS Laser Equipment
ZS Laser Equipment

WhatsApp
Scan the QR Code to start a WhatsApp chat with us.