Laser welding machines are widely used in modern manufacturing due to their high speed, clean weld appearance, and ease of operation. They perform extremely well on many common materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
However, laser welding is not a universal solution. In certain applications, material conditions, thickness requirements, working environments, or quality standards may limit its effectiveness.
Understanding when laser welding is not recommended helps manufacturers choose the right process, avoid unnecessary risks, and achieve more reliable results.
Below are four situations where laser welding may not be the best choice, or where sample testing is strongly advised before production.
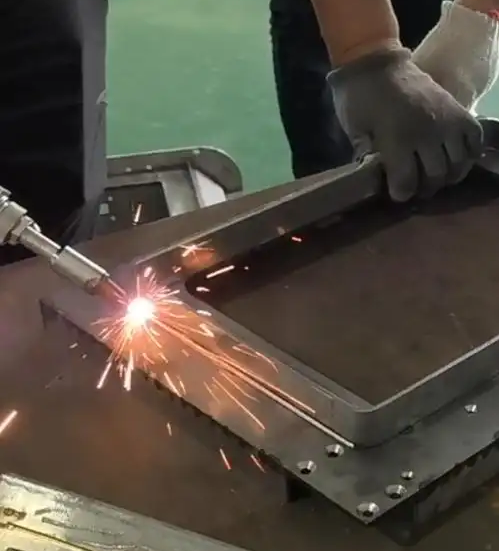

Laser Welding process
1. Unsuitable Materials for Laser Welding
Galvanized steel (hot-dip galvanized materials)
Laser welding galvanized steel often causes heavy spatter and zinc vaporization, which can:
Damage the protective lens more quickly
Increase maintenance frequency
Shorten consumable lifespan compared to welding non-coated materials
Although process optimization and parameter adjustments can reduce these effects, the protective lens life will still be significantly shorter than when welding carbon steel or stainless steel.
Special metals requiring testing
Some materials are not impossible to laser weld, but they require prior sample testing, such as:
Titanium
Magnesium
Nickel
Tin
These materials have specific thermal and metallurgical behaviors that can affect weld quality.
✅ Recommended materials without concern:
Carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum are generally very suitable for laser welding and can achieve stable, high-quality results in most applications.
2. Material Thickness Limitations
Very thin materials (below 0.3 mm)
When material thickness is below 0.3 mm, laser welding becomes challenging:
High risk of burn-through
Very low tolerance for parameter fluctuation
Requires precise control and skilled setup
This does not mean burn-through will always occur, but the process window is extremely narrow, making it less forgiving in mass production.
Very thick materials (above 8 mm)
For materials thicker than 8 mm, laser welding may face limitations in:
Penetration depth
Weld strength
Structural reliability
In such cases, traditional welding methods or hybrid processes may provide better mechanical performance.
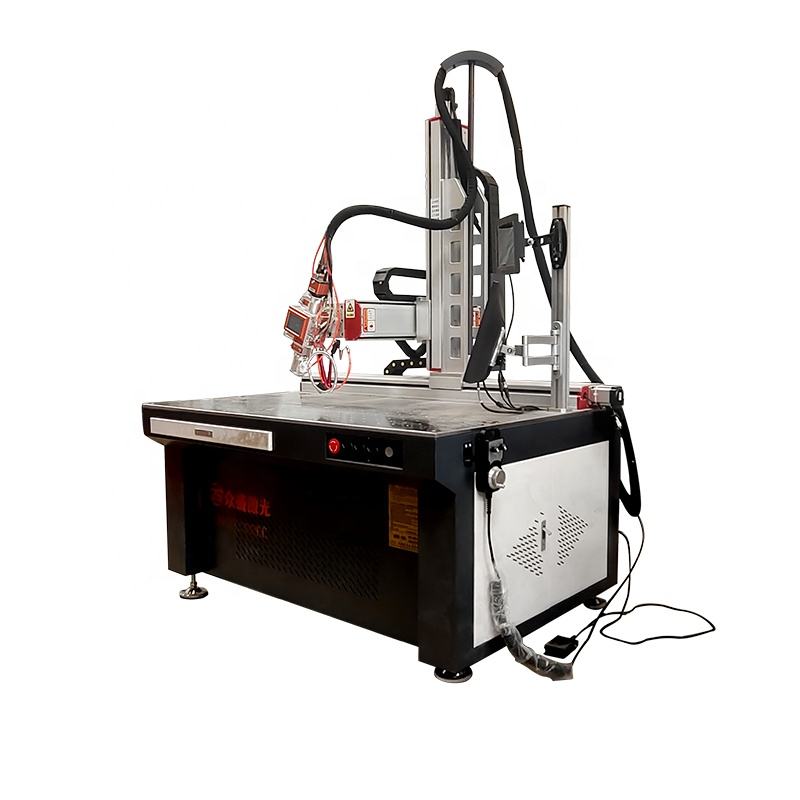

Automatic Laser Welding Machine
3. Unsuitable Working Environments
Strong magnetic environments
Laser welding machines are not ideal for strong magnetic fields, which may:
Interfere with machine operation
Increase the risk of system instability or faults
Reduce overall equipment reliability
Outdoor and on-site welding applications
Laser welding is generally not recommended for outdoor installation work, such as:
Outdoor pipeline welding
Gas tank installation
Fire protection pipe systems
Reasons include:
The laser welding gun is relatively large
Pipes are usually fixed in position
Gun movement is less flexible compared to traditional welding torches
In these scenarios, conventional welding methods often offer better maneuverability and practicality.
4. Special Process and Inspection Requirements
In applications where non-destructive testing (NDT) is mandatory—such as ultrasonic or X-ray inspection—laser welding may face challenges if the process requires:
Absolutely no porosity
No internal voids
No sand holes or gas pores
Achieving such strict internal quality standards with laser welding can be difficult, especially for certain joint designs and materials. In these cases, process validation through testing is essential.
Final Recommendation: Test Before You Decide
If your application does not fall into the four situations above, laser welding is generally a safe and efficient choice.
If your project does fall into one or more of these conditions, it does not automatically mean laser welding is impossible—but sample testing is strongly recommended to verify weld quality, strength, and long-term reliability before full-scale production.
Choosing the Right Laser Welding Solution with ZS Laser
At ZS Laser, we believe that the best welding solution is the one that truly fits your application—not simply the newest technology.
We support customers by:
Evaluating material suitability
Advising on thickness and process limitations
Conducting sample welding tests when needed
Providing realistic, application-driven recommendations
If you are considering laser welding for your project and want to confirm whether it is the right choice, ZS Laser is ready to help you make a confident and informed decision.
Feel free to contact us for technical consultation or sample testing support.
 ZS Laser Equipment
ZS Laser Equipment

WhatsApp
Scan the QR Code to start a WhatsApp chat with us.